
It is exclusively seen at the extremities of long bones like in the femur. Within flat bones such as the cranium, it is distributed throughout the bone. Spongy bone is found specifically near the articular cartilage, at the ends of long bones, pelvic bones, ribs, skull bones, and spinal vertebrae. The human body contains two types of bones: flat bones and long bones. The human body is composed of cancellous or sponge-like bones. It is present in the majority of bone structures and regions that are not susceptible to intense mechanical stress. Compact bone functions to provide strength and protection to bones. Where is spongy bone found? 20% of the human skeleton is composed of cancellous bone, which provides mechanical support as well as mobility without the load on compact bone. It is composed of thin plates and bars of bone adjacent to small, irregular cavities that house red bone marrow.įrom a histological standpoint, spongy bone is composed of thin and interconnected bony spicules referred to as trabeculae, which encase both blood vessels and marrow. However, unlike compact bone, the spongy bone does not possess a central canal. The Haversian canal or central canal is present in the center of each osteon of compact bone tissue, and it serves as a channel for blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. The long bones in a human can develop through this process during embryonic life. Osteoblasts, which are bone cells that make the material that makes up the compact bone matrix, can turn soft sponge bone into mature bone cells and then into hard bone. Osteocytes located near blood arteries can collect nutrients and expel waste via canaliculi, which are microscopic linked tubes on the surface of trabeculae. Blood cell-forming tissue in spongy bone is the red marrow. In spongy bone tissue, lacunae refer to small spaces within the trabeculae that contain osteocytes.īlood veins go through the denser, solid bone to the softer, sponge-like bone, supplying it with the components needed to produce blood cells. Image Credit: OpenStax College (left) and SEER.

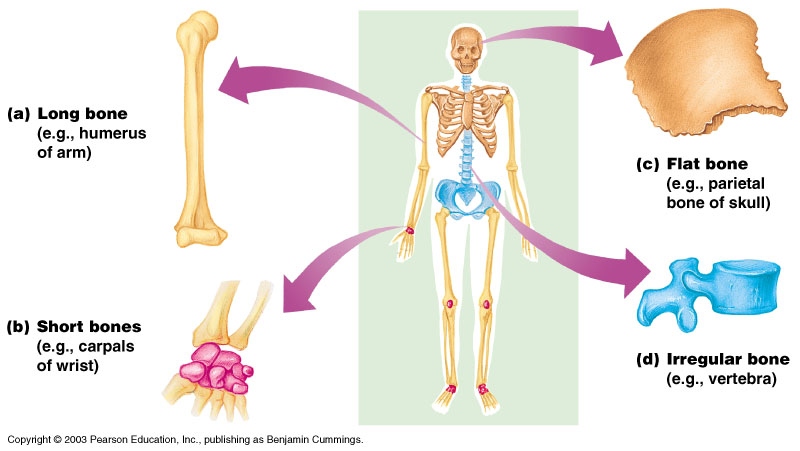
(Britannica, 2023)įigure 1: The long bone diagram: internal structure of a human long bone. The interstices are frequently packed with bone marrow and blood vessels (arteries). The bone matrix or framework is composed of a 3-D latticework of bony tissue termed trabeculae aligned along stress lines. Spongy bone is a porous and light bone containing several big gaps that give the impression of being honeycombed or spongy. Spongy bone structure and spongy bone anatomy are explained below.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
